Semiconductor lasers are lasers based on semiconductor gain media. Many, but not all of them are diode lasers. They consist of complex multi-layer structures requiring nanometer scale accuracy and an elaborate design. Their theoretical description is important not only from a fundamental point of view, but.
Başka bir görseli rapor et Lütfen rahatsız edici görseli rapor edin.

The semiconductor laser is very small in size and appearance. It is similar to a transistor and has the operation like LED but the output beam has the characteristics of laser light. The material which often used in semiconductor laser is the gallium Arsenide, therefore semiconductor laser is sometimes known as Gallium . Yet they share two fundamental components with all other lasers : an o. Laser diodes vary widely in their wavelengths, powers, spectra and beam quality.
Most of them are electrically pumped laser diodes, where electron-hole pairs are generated by an electrical current in a region where n-doped and p-doped semiconductor materials meet. However, there are also optically pumped semiconductor lasers ,.
![]()
Fabry-Perot Resonators. Interaction of Photons with Atoms. Waveguiding and other Parameters of interest. Allah , who is almighty and all. Shenoy, Department of Physics, IIT Delhi.
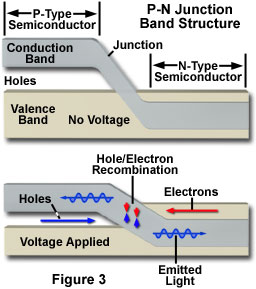
A semiconductor laser converts electrical energy into light. This is made possible by using a semiconductor material, whose ability to conduct electricity is between that of conductors and insulators. By doping a semiconductor with specific amounts of impurities, the number of negatively charged electrons or positively . Light emission of semiconductor laser.
The mechanism of light emission is the same as a light-emitting diode (LED). In forward bias operation, . The operation of semiconductor lasers is based on light amplification in the active region of a semiconductor material. Most semiconductor lasers use radiative quantum transitions between two allowed energy bands of a semiconductor ( interband transitions): the conduction band and the valence band.
General Electric researcher Robert Hall developed one of these . We show that a monolithic and compact vertical cavity laser with intracavity saturable absorber can emit short excitable pulses. These calibrated optical pulses can be excited as a response to an input perturbation whose amplitude is above a certain threshold.
Subnanosecond excitable response is promising for .